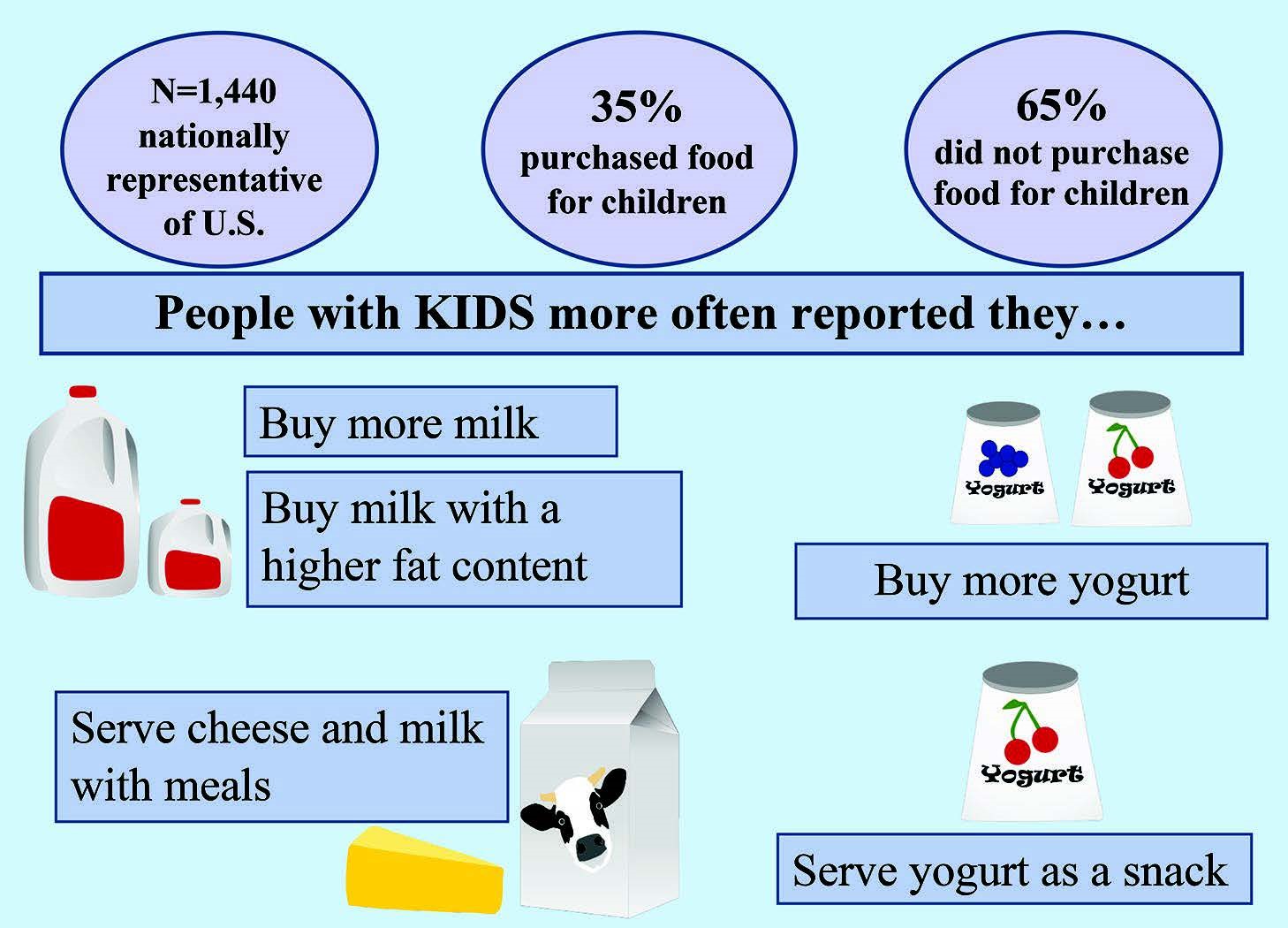
Households with children reported purchasing larger quantities of and higher-fat fluid milk compared to households without children, according to research in JDS CommunicationsTM
Champaign, IL, January 15, 2021 – American dairy consumers are often influenced by a variety of factors that can affect their buying habits. These factors include taste, preference, government information, cultural background, social media, and the news. In an article appearing in JDS Communications, researchers found that households that frequently bought food for children are interested in dairy as part of their diet and purchased larger quantities of fluid milk and more fluid milk with a higher fat content.
To assess the purchasing habits of households that purchase food for children versus those that do not, researchers from Purdue University and Oklahoma State University collected data through an online survey tool, Qualtrics. Respondents, required to be 18 years of age or older, were asked a variety of questions to collect demographic information and dairy product purchasing behavior from US residents. Kantar, an online panel database, was used to obtain participants through their opt-in panel database. “The sample was targeted to be representative of the US population in terms of sex, age, income, education, and geographical region of residence as defined by the US Census Bureau (2016),” said author Mario Ortez, PhD student at Purdue University in West Lafayette, IN, USA.
The survey received a total of 1,440 responses to be assessed. Per the results, 511 respondents indicated they frequently purchased food specifically for children, whereas 929 indicated they did not. Of the 1,440 respondents, 521 indicated that they had at least one child in the household, and 912 indicated they did not have children in their household. The study found that households that frequently purchased food for children generally purchased larger quantities of fluid milk, along with their chosen fluid milk having a higher fat content. Households with children also bought yogurt more frequently than other households.
Caption: A new study published in JDS Communications found that households with children reported purchasing larger quantities and higher-fat dairy products compared to households without children (Credit JDS Communications).
Other findings from the survey indicated that cheese and milk are most often purchased for part of a meal, and yogurt is bought most frequently as a snack. The survey also found that households largely reported reviewing product attributes of price, expiration date, and nutritional information (in that order) on egg, milk, and meat labels.
“This study demonstrates the continued belief among American consumers that dairy products are an important part of a healthy diet fed to children. The popularity of whole milk, cheese, and yogurt within these households suggests that children enjoy the taste of dairy products and are happy to have them served during regular meals and at snack time,” said Matthew Lucy, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of JDS Communications, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, USA. These findings can influence product marketing efforts and stakeholder decisions in the dairy industry.
“Future studies can build on this work by evaluating whether there is a spillover effect from purchasing specifically for children and the general dairy and protein product purchasing habits of those households,” said Dr. Courtney Bir, PhD, coauthor of the study and assistant professor, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA.
Policy makers and companies can use this information to help inform product labeling and better target necessary segments to increase product awareness and better the dairy industry as a whole.
Notes for editors
The article is “Dairy product purchasing in households with and without children,” by Mario Ortez, Courtney Bir, Nicole Olynk Widmar, and Jonathan Townsend (https://doi.org/10.3168/jdsc.2020-19305). It appears in JDS Communications, volume 2, issue 1 (January 2021), published by FASS Inc. and Elsevier.
The article is openly available at www.jdscommun.org/article/S2666-9102(21)00001-6/fulltext.
Full text of the article is also available to credentialed journalists upon request. Contact Eileen Leahy at +1 732 238 3628; jdsmedia@elsevier.com or Ken Olson at +1 630 237 4961; keolson@prodigy.net to obtain copies. Journalists wishing to interview the authors should contact the corresponding author, Mario Ortez, Purdue University, at mortez@purdue.edu.
About JDS Communications
An official journal of the American Dairy Science Association®, JDS Communications is an Open Access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes short, concise original research in the form of short communications, technical notes, mini-reviews, and other scholarly works that relate to the production and processing of milk or milk products intended for human consumption. Research published in this journal is broadly divided into animal production, physiology, health, and genetics and dairy foods for human consumption. www.jdscommun.org
About the American Dairy Science Association (ADSA®)
The American Dairy Science Association (ADSA) is an international organization of educators, scientists, and industry representatives who are committed to advancing the dairy industry and keenly aware of the vital role the dairy sciences play in fulfilling the economic, nutritive, and health requirements of the world's population. It provides leadership in scientific and technical support to sustain and grow the global dairy industry through generation, dissemination, and exchange of information and services. Together, ADSA members have discovered new methods and technologies that have revolutionized the dairy industry. www.adsa.org
About Elsevier
Elsevier is a global information analytics business that helps scientists and clinicians to find new answers, reshape human knowledge, and tackle the most urgent human crises. For 140 years, we have partnered with the research world to curate and verify scientific knowledge. Today, we’re committed to bringing that rigor to a new generation of platforms. Elsevier provides digital solutions and tools in the areas of strategic research management, R&D performance, clinical decision support, and professional education; including ScienceDirect, Scopus, SciVal, ClinicalKey, and Sherpath. Elsevier publishes over 2,500 digitized journals, including The Lancet and Cell, 39,000 e-book titles and many iconic reference works, including Gray’s Anatomy. Elsevier is part of RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers. www.elsevier.com
About FASS Inc.
Since 1998, FASS has provided shared management services to not-for-profit scientific organizations. With combined membership rosters of more than 10,000 professionals in animal agriculture and other sciences, FASS offers clients services in accounting, membership management, convention and meeting planning, information technology, and scientific publication support. The FASS publications department provides journal management, peer-review support, copyediting, and composition for this journal; the staff includes five BELS-certified (www.bels.org) technical editors and experienced composition staff. www.fass.org