Potential for the development of tailor-made fermented milks to help reduce hypertension, according to the Journal of Dairy Science®
Philadelphia, March 14, 2021 – In recent years, fermented dairy foods have been gaining attention for their health benefits, and a new review published in the Journal of Dairy Science indicates these foods could help reduce conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure). A team of investigators from the Center for Food Research and Development in Sonora, Mexico, and the National Technological Institute of Mexico in Veracruz report on numerous studies of fermented milks as antihypertensive treatments and in relation to gut microbiota modulation. They also examine the potential mechanistic pathways of gut modulation through antihypertensive fermented milks.
In addition to the impact of genetics and the environment, there is growing evidence that gut microbiota may also have an effect on the development of hypertension. In this sense, gut dysbiosis (a marked decrease in richness and diversity of the gut microbiota) has been linked to different metabolic diseases, including hypertension.
“Several studies have indicated that fermented milks may positively affect gut microbiota or provide antihypertensive effects,” explained investigator Belinda Vallejo-Córdoba, PhD, of the Center for Food Research and Development. “However, few studies have shown a link between the antihypertensive effect of fermented milks and induced microbial balance (or eubiosis). Remarkably, the antihypertensive effect has been attributed mainly to ACEI peptides, and few studies have attributed this effect to gut modulation.”
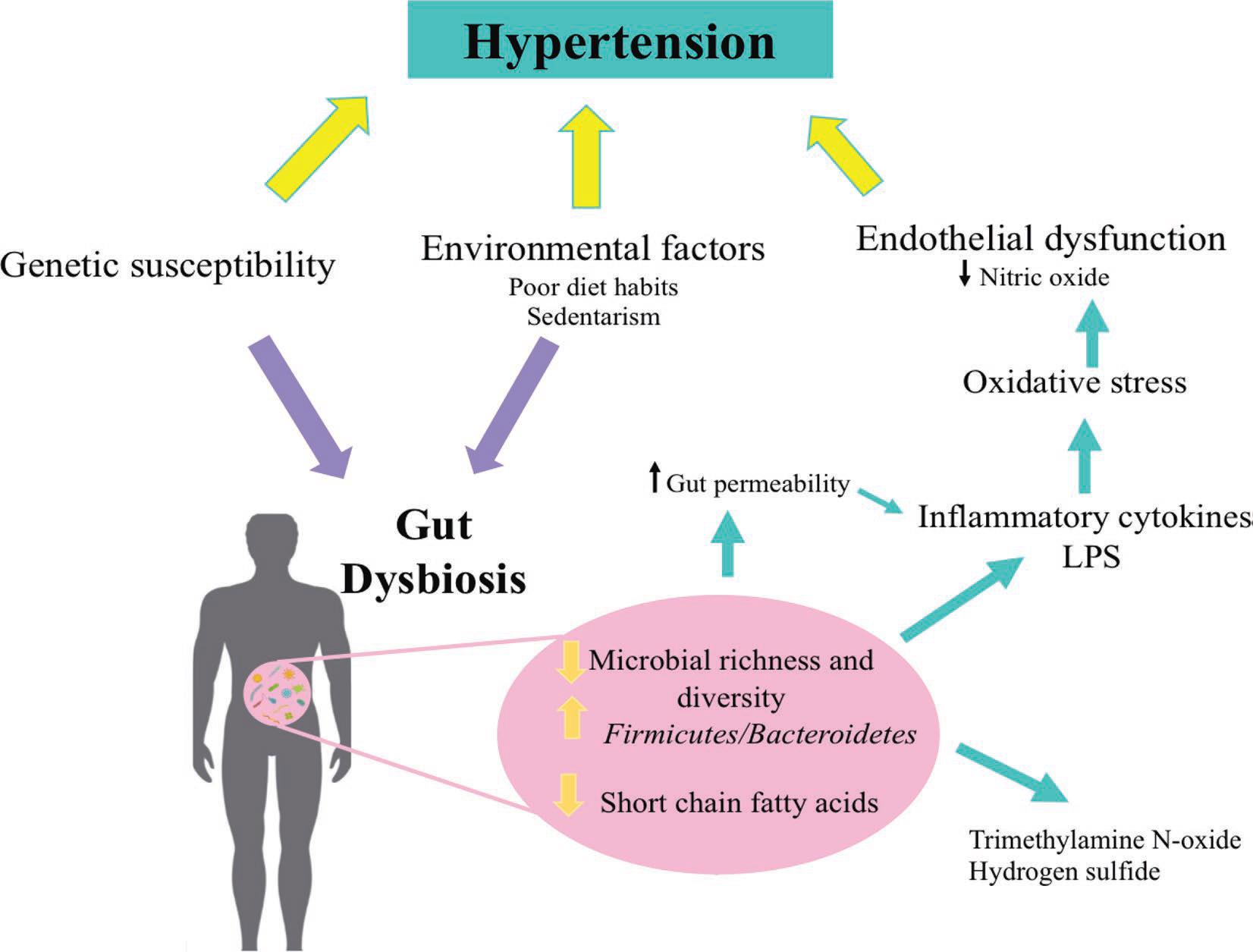
Caption: Association between dysbiosis of gut microbiota and hypertension (Credit: Journal of Dairy Science).
“New evidence suggests that antihypertensive fermented milks, including probiotics, bioactive peptides, and exopolysaccharides obtained from milk fermented with specific lactic acid bacteria, may modulate gut microbiota. Therefore, there is potential for the development of tailor-made fermented milks with gut microbiota modulation and blood pressure-lowering effects,” added Vallejo-Córdoba.
The authors say that future studies are needed to help understand the antihypertensive effects of fermented milks.
Hypertension is a risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease and is one of the leading causes of death globally. Gut microbiota have been found to influence intestinal development, barrier integrity and function, body metabolism, the immune system and the central nervous system. A microbial imbalance affects metabolism, which may lead to metabolic diseases like hypertension, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
Notes for editors
The article is “Invited review: Effect of antihypertensive fermented milks on gut microbiota,” by Lilia M. Beltrán-Barrientos, Hugo S. García, Adrián Hernández-Mendoza, Aarón F. González-Córdova, and Belinda Vallejo-Cordoba (https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-19466). It appears in the Journal of Dairy Science, volume 104, issue 4 (April 2021), published by FASS Inc. and Elsevier.
Full text of the article is available to credentialed journalists upon request. Contact Eileen Leahy at +1 732 238 3628 or jdsmedia@elsevier.com to obtain copies. Journalists wishing to interview the authors should contact the corresponding author, Belinda Vallejo-Córdoba, at vallejo@ciad.mx.
The study was supported by CONACyT research projects 240338 and 60305.
About the Journal of Dairy Science
The Journal of Dairy Science® (JDS), an official journal of the American Dairy Science Association®, is co-published by Elsevier and FASS Inc. for the American Dairy Science Association. It is the leading general dairy research journal in the world. JDS readers represent education, industry, and government agencies in more than 70 countries, with interests in biochemistry, breeding, economics, engineering, environment, food science, genetics, microbiology, nutrition, pathology, physiology, processing, public health, quality assurance, and sanitation. JDS has a 2019 Journal Impact Factor of 3.333 and 5-year Journal Impact Factor of 3.432 according to Journal Citation Reports (Source: Clarivate 2020). www.journalofdairyscience.org
About the American Dairy Science Association (ADSA)
The American Dairy Science Association (ADSA) is an international organization of educators, scientists, and industry representatives who are committed to advancing the dairy industry and keenly aware of the vital role the dairy sciences play in fulfilling the economic, nutritive, and health requirements of the world's population. It provides leadership in scientific and technical support to sustain and grow the global dairy industry through generation, dissemination, and exchange of information and services. Together, ADSA members have discovered new methods and technologies that have revolutionized the dairy industry. www.adsa.org
About Elsevier
As a global leader in information and analytics, Elsevier helps researchers and healthcare professionals advance science and improve health outcomes for the benefit of society. We do this by facilitating insights and critical decision-making for customers across the global research and health ecosystems.
In everything we publish, we uphold the highest standards of quality and integrity. We bring that same rigor to our information analytics solutions for researchers, health professionals, institutions and funders.
Elsevier employs 8,100 people worldwide. We have supported the work of our research and health partners for more than 140 years. Growing from our roots in publishing, we offer knowledge and valuable analytics that help our users make breakthroughs and drive societal progress. Digital solutions such as ScienceDirect, Scopus, SciVal, ClinicalKey and Sherpath support strategic research management, R&D performance, clinical decision support, and health education. Researchers and healthcare professionals rely on our 2,500+ digitized journals, including The Lancet and Cell; our 40,000 eBook titles; and our iconic reference works, such as Gray's Anatomy. With the Elsevier Foundation and our external Inclusion & Diversity Advisory Board, we work in partnership with diverse stakeholders to advance inclusion and diversity in science, research and healthcare in developing countries and around the world.
Elsevier is part of RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers. www.elsevier.com
About FASS Inc.
Since 1998, FASS has provided shared management services to not-for-profit scientific organizations. With combined membership rosters of more than 10,000 professionals in animal agriculture and other sciences, FASS offers clients services in accounting, membership management, convention and meeting planning, information technology, and scientific publication support. The FASS publications department provides journal management, peer-review support, copyediting, and composition for this journal; the staff includes five BELS-certified (www.bels.org) technical editors and experienced composition staff. www.fass.org